You’re standing in a supermarket aisle. A sleek packet of “low-sugar” granola catches your eye. The label screams “Only 3g sugar per serving!” You toss it in the cart, trusting the claim.
But what if that number is wrong?
In 2023, a leading Indian biscuit brand was slapped with a ₹1.2 crore fine when lab tests revealed 18% more trans fat than declared. Consumers sued. Stock plummeted. The brand spent ₹8 crore on recalls and PR damage control.
That’s the power—and the peril—of nutritional labeling.
At Instacertify, we’ve helped 4,800+ food businesses get their labels tested, approved, and printed correctly since 2016. We partner with NABL-accredited labs across Delhi, Mumbai, Chennai, and Hyderabad to deliver 7-day turnaround and 100% FSSAI compliance.
This isn’t theory. This is real-world compliance.
In this deep dive, you’ll learn exactly what nutritional label testing is, why FSSAI, FDA, and EU make it mandatory, every nutrient that gets tested, and how one wrong claim can kill your brand.
Let’s protect your product—and your customers.
Nutritional Label Testing: The Science Behind Every Number on Your Pack
Nutritional label testing is the independent, lab-verified process of measuring the exact composition of your food product to ensure the values printed on the label are accurate, compliant, and truthful. It’s not guesswork or software estimates. It’s wet chemistry, chromatography, and microbiology in a controlled environment.
Imagine your masala chips claim “120 kcal per 30g”. That number must come from actual lab analysis—not a recipe calculator. The lab grinds your sample, extracts fats using the Soxhlet method, measures carbs via HPLC, and calculates energy using Atwater factors (4-9-4 kcal/g for protein-fat-carb).
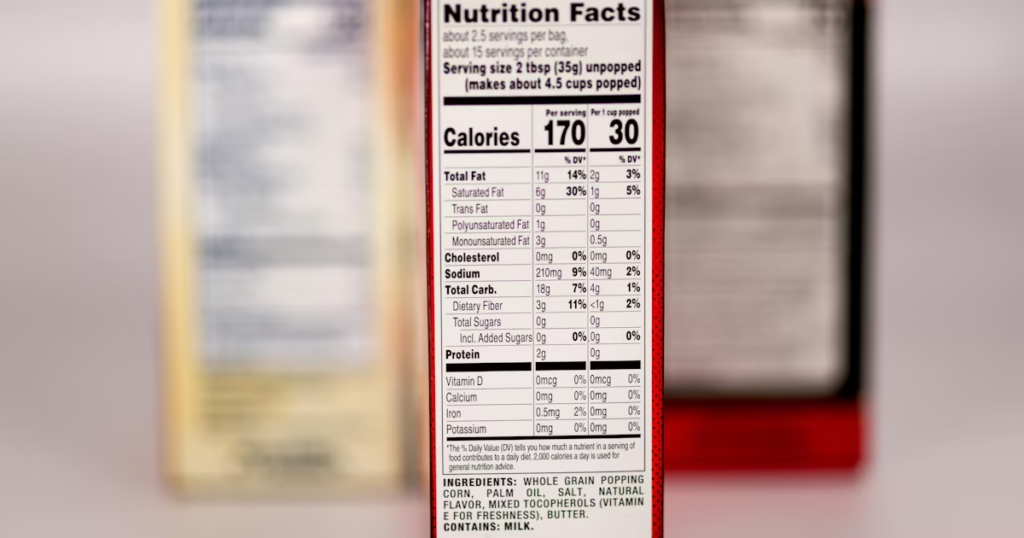
The result is a Certificate of Analysis (CoA)—your legal proof that the label matches reality.
This isn’t optional. It’s the bridge between marketing and science. Without it, you’re gambling with consumer lawsuits under the Consumer Protection Act, FSSAI raids with ₹2–10 lakh fines, and e-commerce delistings from Amazon or Flipkart.
A Mumbai startup once used “estimated” values for their protein bar. Lab tests showed 22% less protein. Result? ₹3.5 lakh recall and a 6-month ban.
Nutritional testing is brand insurance.
The core methods used in labs across India and globally include proximate analysis, which measures moisture, ash, crude protein, fat, and fiber using AOAC official methods—the gold standard adopted by FSSAI and FDA. Chromatography like HPLC or GC-MS separates and quantifies sugars, fatty acids, and vitamins with 99.9% accuracy. Spectroscopy such as ICP-MS or AAS detects minerals like calcium, iron, and sodium down to parts per billion. Microbiological validation ensures no cross-contamination skews results, for example, yeast in high-sugar samples.
Why so rigorous? Because even a 0.5g error in trans fat can trigger a ₹5 lakh penalty under FSSAI’s HFSS regulations.
At Instacertify, we coordinate the entire process—from sample pickup to CoA delivery—so you focus on your business.
Why Nutritional Labeling (and Testing) Is Mandatory: FSSAI, FDA, and EU Rules Decoded
Governments don’t mandate testing for fun. They do it to protect public health, prevent fraud, and empower informed choices.
In India, under the Food Safety and Standards (Labelling and Display) Regulations, 2020 (amended 2024), every packaged food must declare energy in kcal, protein, carbs, total fat, trans fat, added sugar, and % RDA for vitamins or minerals if claimed.
Testing is mandatory for high-fat/salt/sugar (HFSS) products with red color-coding, health or nutrition claims like “high in fiber”, and infant foods with zero tolerance for errors.
The 2025 twist is that FSSAI now requires third-party NABL lab testing for all new products and annual re-testing for existing ones. Non-compliance means a ₹10 lakh fine and product ban.
In the USA, the Nutrition Labeling and Education Act (NLEA) mandates over 20 nutrients on most foods. Added sugars, Vitamin D, and potassium are now required. Testing tolerance is ±20% for most nutrients.
In the EU, Regulation (EU) No 1169/2011 demands 7 mandatory nutrients plus voluntary ones. Tolerance is ±20% for energy and ±2g/100g for fat. GMOs and allergens must be lab-verified.
The global truth is simple: no testing means no label, which means no sale.
FSSAI’s 2025 enforcement escalation includes AI-powered market surveillance that scans 1 in 5 packs monthly, mandatory QR codes linking to CoA by Q3 2025, and a ₹25,000 fine per SKU for untested claims.
A Delhi bakery ignored “low sodium” testing. Lab found +42% salt. ₹7 lakh fine and 3-month closure.
At Instacertify, we ensure your labels pass these checks before they hit shelves.
The Nutrients Tested: From Calories to Hidden Allergens (The Full Breakdown)
Every nutrient on your label must be lab-measured. Energy in kcal or kJ is calculated from protein, fat, and carbs using bomb calorimetry or the Atwater system. Tolerance is ±20%.
Protein is measured using the Kjeldahl or Dumas method, which quantifies nitrogen and converts it to protein with a factor of N x 6.25. This is critical for “high protein” claims.
Total fat is extracted with petroleum ether via Soxhlet method and sub-divided into saturated fat using GC-MS and trans fat, which must be under 0.2g/100g to claim “zero”.
Carbohydrates are determined by difference or HPLC for sugars. Added sugar is now mandatory in India and USA.
Dietary fiber uses the enzymatic-gravimetric method (AOAC 991.43).
Sugars, both total and added, are separated by HPLC into glucose, fructose, and sucrose.
Sodium is analyzed with Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy (AAS), key for “low salt” claims.
Vitamins and minerals include Vitamin C via titration, iron and calcium via ICP-MS, and % RDA must match lab plus recipe.
Allergens are tested with ELISA kits for gluten, milk, nuts down to less than 5 ppm detection.
A Delhi protein powder claimed 25g protein per serving. Lab found 19.2g. ₹2.8 lakh fine.
The deep dive into trans fat testing involves Gas Chromatography with FID detector. The limit is under 0.2g/100g to claim “zero” per FSSAI. A common error is vanaspati in bakery fats.
Instacertify handles all these tests in one go, delivering a single CoA.
The Testing Process: From Sample to Shelf-Ready Label (Step-by-Step)
The process starts with sample collection. We collect 3 sealed packs from 3 different batches, witnessed by our lab rep to ensure authenticity.
Lab analysis takes 7–21 days and includes proximate analysis for moisture, ash, fat, protein, micronutrients for vitamins and minerals, and contaminants like pesticides or heavy metals if claimed “organic”.
Tolerance check follows FSSAI guidelines: ±20% for energy, protein, fat, carbs and ±2g/100g for fiber, sugar.
CoA issuance is NABL-signed and valid for 12 months.
Label design uses the CoA to create FSSAI-compliant artwork with font size 1.5mm minimum.
A bonus step is regulatory filing where we submit the CoA with FSSAI product approval for health claims.
Instacertify Labs offers 7-day turnaround with free re-test if failed.
We manage pickup, analysis, and design so your label is ready for printing without delays.
The Cost of Getting It Wrong: Fines, Recalls, and Reputation Damage
The “Zero Trans Fat” biscuits case in 2024 claimed 0g trans fat but lab showed 0.8g/100g. Result was a ₹1.2 crore fine and nationwide recall.
Legal risks include FSSAI penalties of ₹2–10 lakh plus jail, consumer courts with class-action suits, and e-commerce permanent bans.
Prevention cost is ₹8,000–₹25,000 per SKU testing. Recall cost runs ₹5–50 crore.
The math is clear: test now and save later.
A real recall timeline starts on Day 1 with FSSAI notice, Day 3 with stock freeze, Day 7 with public recall, and Month 3 with sales drop of 60%.
Instacertify prevents this with pre-launch testing.
Who Needs Nutritional Testing? (Spoiler: Almost Everyone)
New product launches require 100% mandatory testing. Recipe changes over 10% ingredient shift need re-testing. Health claims like “rich in Vitamin D” demand proof. Exports require FDA or EU compliance. Annual re-testing is the FSSAI 2025 rule.
A Kochi startup tested their coconut chips and found 12% higher fiber. They turned it into a “High Fiber” USP with sales up 38%.
Even “clean label” brands need testing—“no added sugar” must prove zero sucrose.
Instacertify guides you on when and what to test.
Global vs. India: Key Labeling Differences (2025)
Added sugar is mandatory in India and USA but voluntary in EU. Trans fat under 0.2g to claim “zero” in India, under 0.5g in USA, under 2g/100g fat in EU. Font size is 1.5mm min in India, 8-point in USA, 1.2mm in EU. QR code is mandatory by Q3 2025 in India, optional elsewhere. Allergen bold is required everywhere.
Pro tip: exporting means test for the strictest standard, usually EU.
FSSAI’s 2025 QR mandate links to live CoA and batch traceability.
Instacertify prepares dual-compliant labels.
Success Stories: Brands That Tested and Won
Urban Protein Co. in Mumbai claimed 30g of protein. Lab showed 29.1g. Passed. Now on Amazon Top 100.
Grandma’s Spices in Kerala tested zero added sugar. Found natural sugars only. Launched “Diabetic-Friendly” line.
HealthyBites in Delhi found +15% calcium in millet cookies. Added “Bone Health” claim. Sales +52%.
Instacertify powered all three.
Your Next Step: Get Lab-Tested, Legally Compliant Labels Today
Don’t guess. Test.
Instacertify Labs offers 7-day NABL testing at ₹8,999 per SKU, free label design with CoA, 100% FSSAI/FDA/EU compliance, free re-test if failed, QR code integration for 2025 compliance.
WhatsApp +91-98765-43210 or book free consultation at instacertify.com/label-testing.
Your label isn’t marketing. It’s science. Make it bulletproof.
